Getting started
Overview
Ostorlab is a security and privacy scanner for mobile applications, web applications, and attack surface discovery.
Three main steps
Discover and manage your infrastructure and external assets: Detect correlations and find other assets you did not even know existed.
Scan mobile, web, and network assets: Ostorlab covers Android and iOS platforms, Web and Web APIs, and network scanning. It can identify over 500 classes of vulnerabilities and 100.000 outdated, vulnerable dependencies. It uses robust static, dynamic and behavioral analysis to ensure high coverage of the application’s attack surface and validate findings to enable false-positive free results.
Remediate: All vulnerabilities get aggregated into tickets that can be assigned to developers on the platform or integrated with an internal ticketing system. You can fix the vulnerability and let Ostorlab verify and confirm the fixes.
Getting Started
- Create an account here using your email address and password.

- The main page is a Dashboard, which gives a view above of what is happening.
It displays:
-
A list of recent scans.
-
A spider graph expressing your organization's performance compared to others in terms of five metrics: Mean resolution time of vulnerabilities, vulnerability severity, percentage of secure apps, rate of exceptions, and rate of reopened vulnerabilities; vulnerabilities showing up again after a fix.
-
A vulnerability trending graph represents the frequency of vulnerabilities being detected and fixed.
-
A calendar and a scan heatmap for organizations with policies and specific compliance programs.
-
To start a scan, head to the New Scan menu and select your asset type.
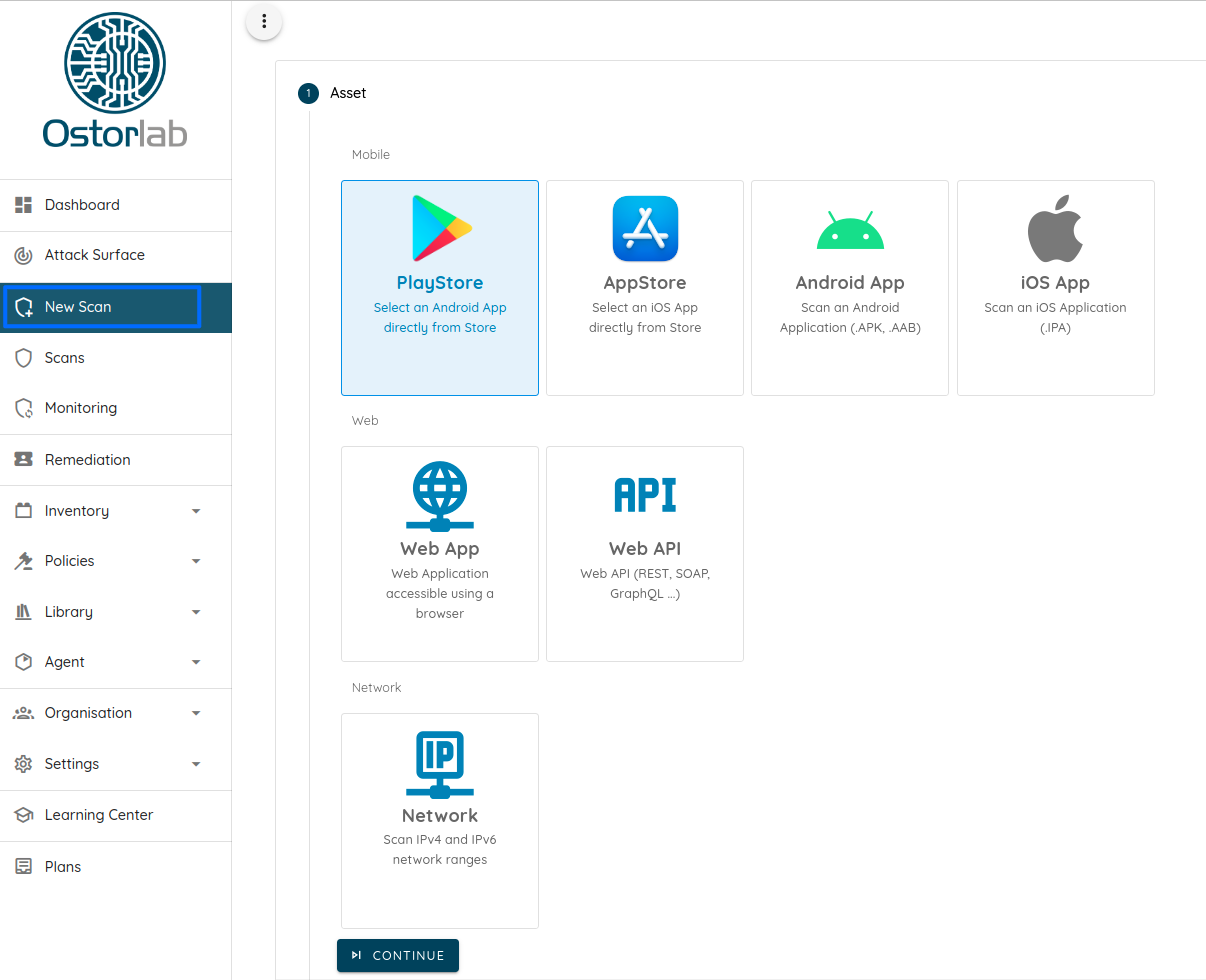
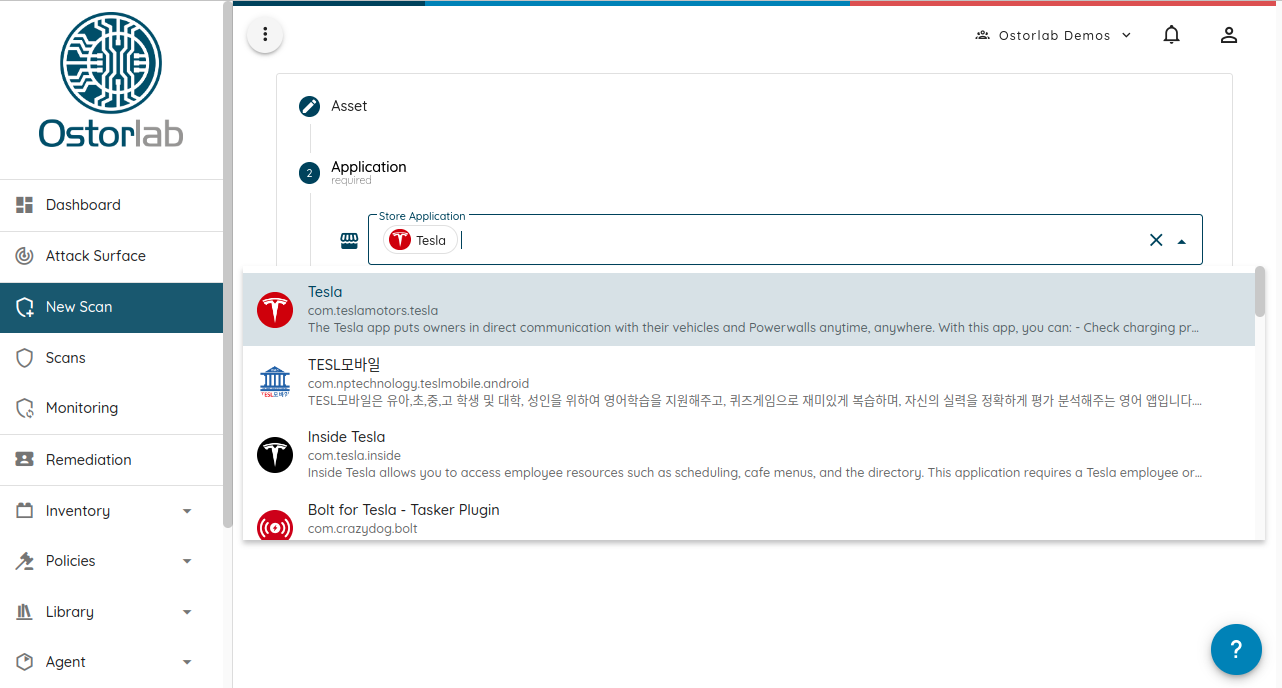
- You then have to select your asset by searching the store, uploading a file, or simply typing the link to your web application or public IP address.
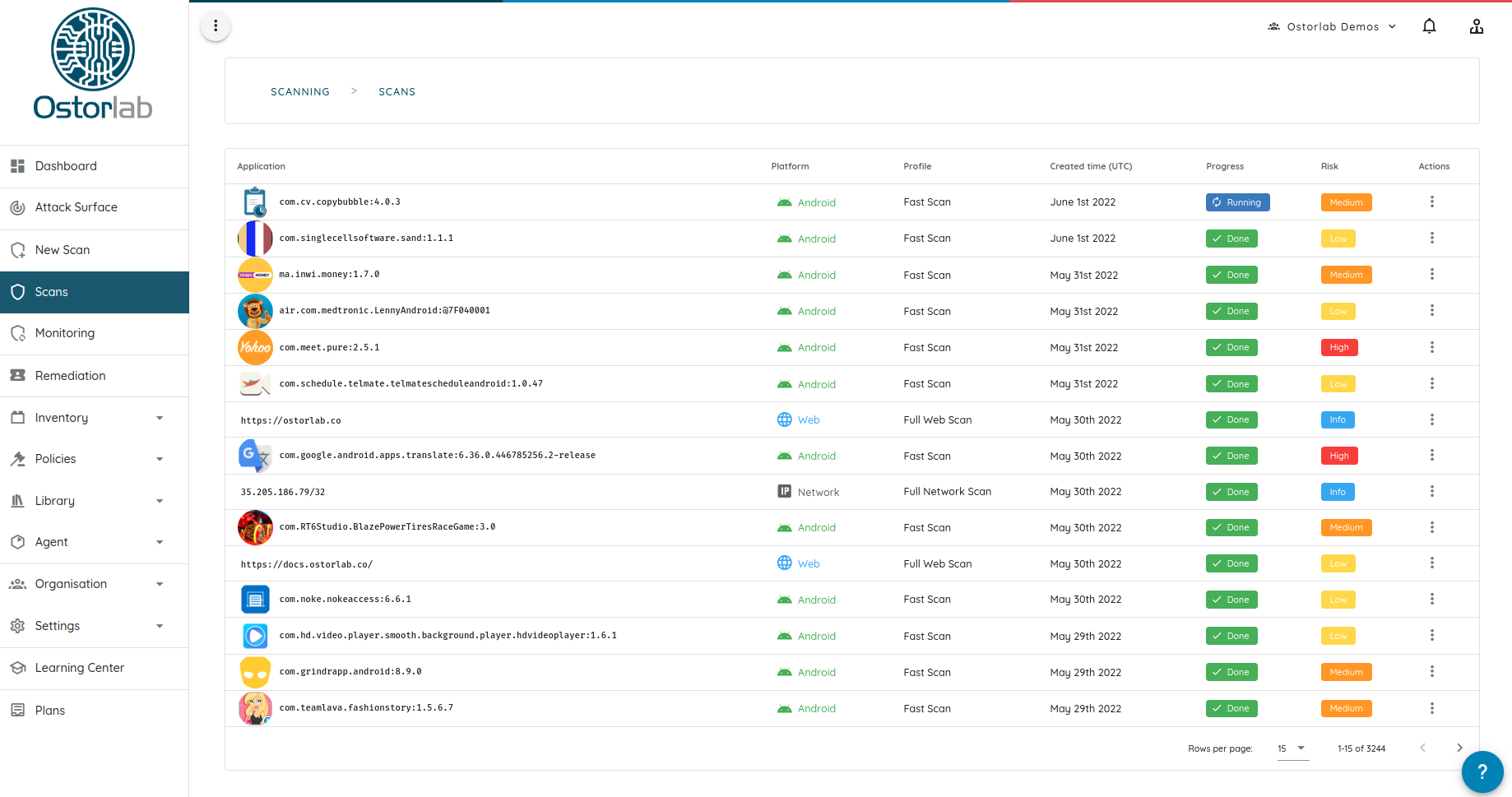
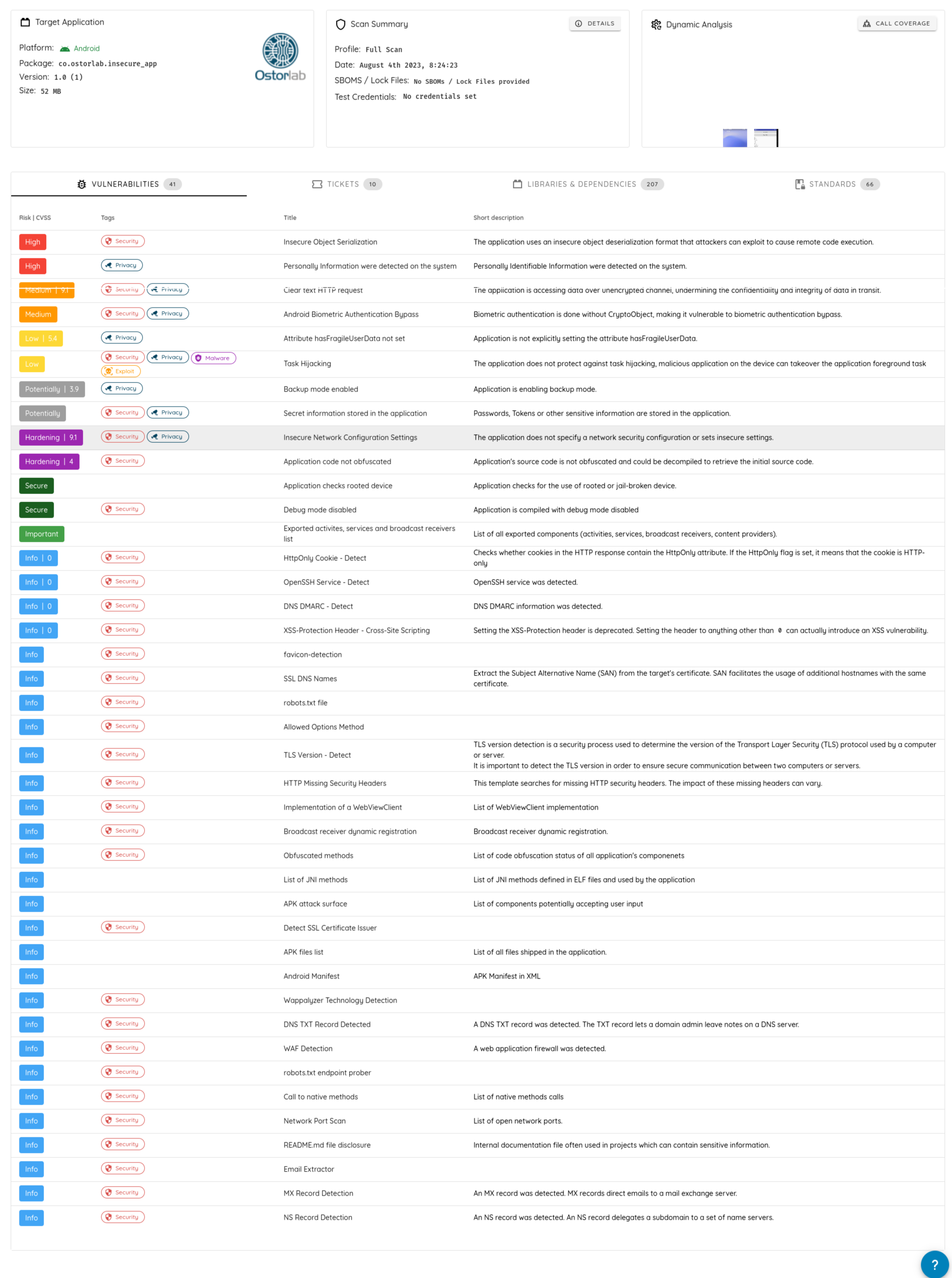
- You can check your scan progress in the Scanning Section, first queued, running, and then done:
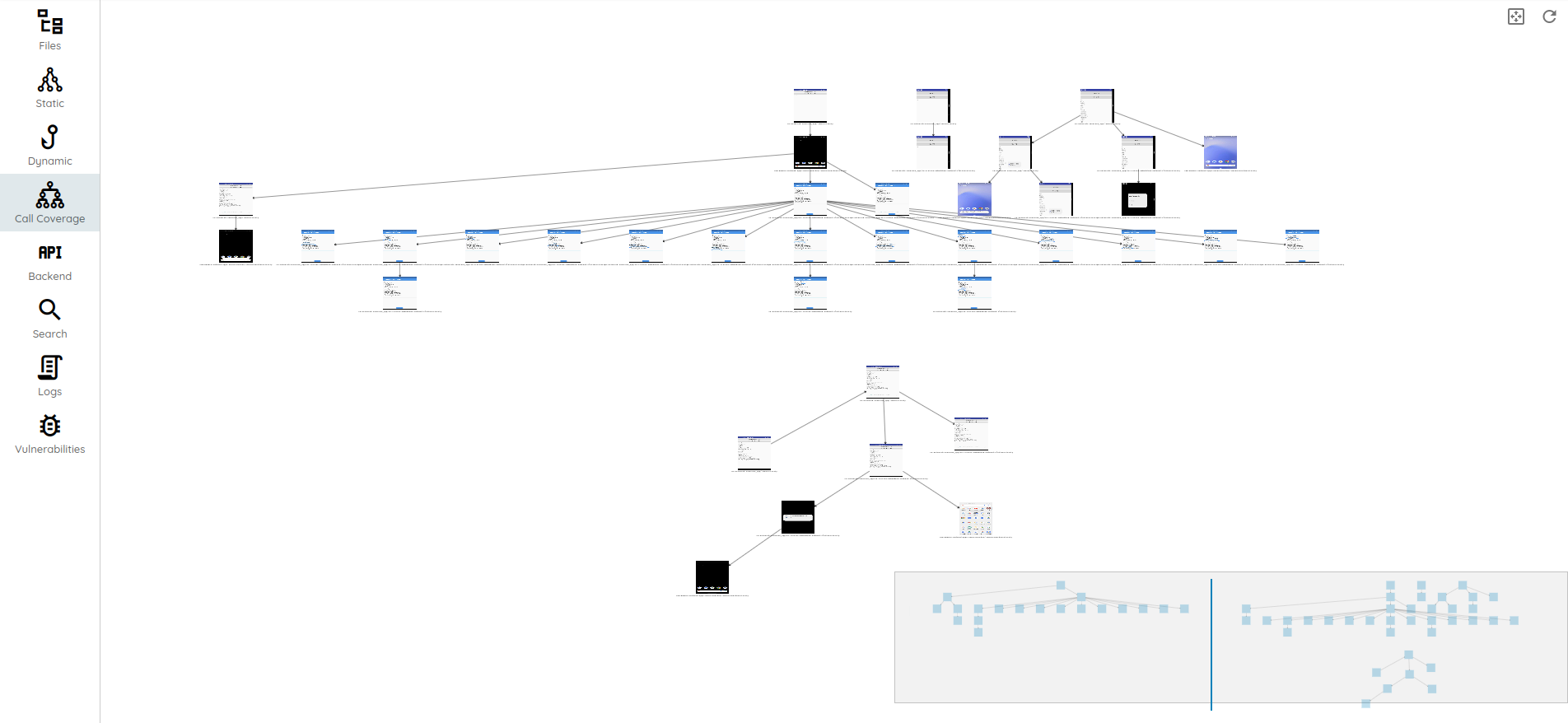
- While the scan is running, you can already start accessing the scan results.
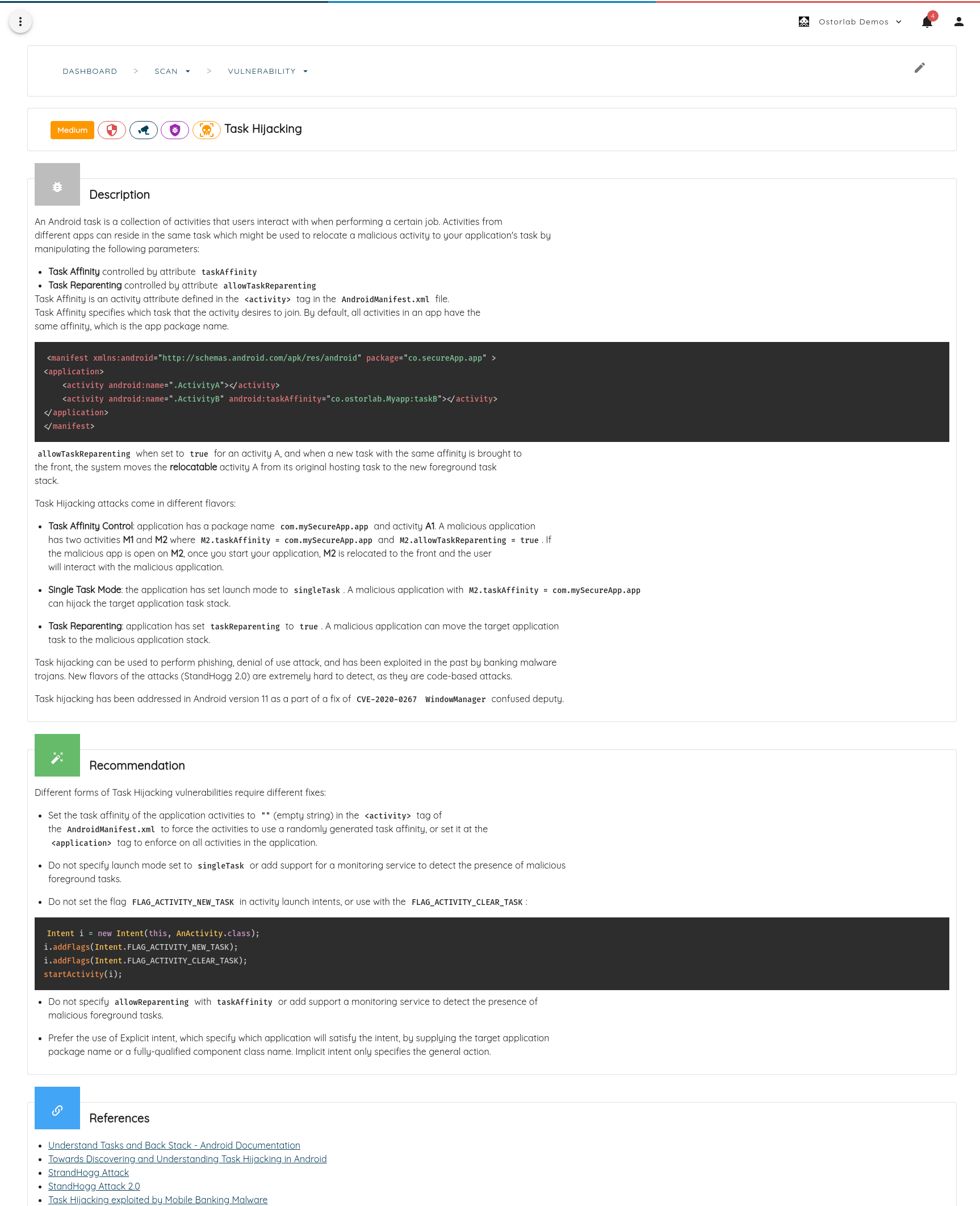
- You may click on any finding to access detailed reports with recommendations, references, and technical details:
- The scans page has three sections:
Vulnerabilities: Lists actionable findings.
Ticket: Lists all the tickets for the scanned asset. It automatically updates the status based on the previous scan.
Dependency: Lists of 3rd party libraries and frameworks fingerprinted in the application.
- You can also access the scan artifacts or generate a PDF report. The PDF generation runs in the background, and you receive a notification once the report is ready.

- All scans produce a set of artifacts that varies depending on the type of the scan.